As the financial landscape evolves, the question arises: what is Fintech? This comprehensive blog post dives deep into the Fintech industry overview, revealing current trends and insights that are shaping its future. Readers will explore the various types of Fintech solutions that are revolutionizing traditional finance, while also uncovering the benefits of Fintech services that enhance both efficiency and accessibility. By understanding Fintech through its core technologies, supported by compelling Fintech examples and applications, financial professionals can stay ahead of the curve in an industry characterized by rapid innovation. Prepare to gain valuable knowledge and insights that will empower your practice and position you for success in the dynamic world of financial technology.
What Is Fintech? A Comprehensive Definition
The term fintech has gained exceptional traction in recent years, becoming a fundamental part of the modern financial landscape. Broadly defined, fintech refers to the integration of technology within the financial services sector, intending to enhance various financial processes. However, its meaning extends beyond mere technology usage; it encapsulates a diverse range of innovations and methodologies aimed at making financial services more efficient, accessible, and user-friendly.
The fintech industry overview illustrates that this sector encompasses a multitude of services that cater to businesses and consumers alike. Here’s a breakdown of what constitutes fintech:
- Digital Banking: Online banks or apps that bypass traditional bank branches, offering services such as savings accounts, loans, and personal finance management.
- Payment Solutions: Technologies that facilitate electronic transactions, including mobile payment apps (like PayPal and Venmo), contactless payments, and cryptocurrency transactions.
- Insurance Technology (Insurtech): Platforms that streamline the insurance process by automating policy management and claims processing.
- Robo-Advisors: Algorithms that provide automated financial planning services with minimal human intervention, often at reduced fees.
- Crowdfunding Platforms: Websites enabling businesses and entrepreneurs to raise funds from a large number of people, typically via small contributions.
- Blockchain Solutions: Distributed ledger technology that enhances transparency and security in transactions, essential for cryptocurrencies and smart contracts.
Although the types of fintech solutions vary widely, they are united by a common goal: improving efficiency within financial services. This efficiency manifests through faster transaction times, reduced costs, and expanded service availability, thus addressing gaps often found in traditional banking.
Understanding fintech encompasses recognizing the benefits of fintech services. Below are the main advantages:
- Increased Accessibility: Fintech platforms break down geographical barriers, providing individuals and businesses in remote areas with access to financial services that were previously unavailable.
- Cost Efficiency: Lower operational costs due to automation lead to decreased fees for consumers, making financial services more affordable.
- Enhanced User Experience: Fintech solutions prioritize user-friendly interfaces and seamless user experiences, making financial transactions straightforward and engaging.
- Speed: Transactions that traditionally took days or weeks can now be completed in real time, thanks to advancements in technology.
- Innovation: Continuous advancements in fintech solutions foster a culture of innovation, which generates better financial products and services.
To visualize the scope of fintech’s impact, the table below summarizes some key components associated with this transformative sector:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Industry Players | Startups, traditional banks, tech companies, and investors. |
| Technological Focus | AI, machine learning, blockchain, mobile applications. |
| Customer Base | Individuals, small businesses, large enterprises, and institutions. |
| Investment | Gravitating towards sustainable and scalable financial technologies. |
In summary, the essence of fintech delves deeper than just definitions; it represents a revolutionary shift in how financial services are structured and delivered. By understanding the definitions, types, and benefits of fintech solutions, professionals in the finance sector can better appreciate the innovations that are shaping the future of their industry.

Fintech Industry Overview: Current Trends and Insights
The fintech industry overview reveals a fast-evolving landscape, driven by technology, consumer demands, and regulatory adaptations. The transformation of financial services through innovation is not just reshaping traditional banking but also influencing how businesses and individuals manage their finances. Here are the key trends and insights defining the fintech sector today:
1. Surge in Digital Payment Solutions
- With the rise of e-commerce and online transactions, digital payment platforms have gained immense traction. Consumers are now accustomed to using mobile wallets and contactless payments for everyday purchases.
- Key players like PayPal, Venmo, and newer entrants such as Apple Pay and Google Pay indicate a shift toward seamless payment experiences.
2. Significant Growth of Neobanks
- Neobanks, which operate exclusively online without physical branches, have emerged as a popular alternative to traditional banks. They offer low-fee or no-fee banking services, tapping into an underserved market.
- Institutions such as Chime and N26 exemplify this trend, emphasizing customer-centric features and innovative user interfaces.
3. Rise of Personal Finance Management Tools
- Empowering consumers to take control of their finances has led to the popularity of personal finance apps like Mint and YNAB (You Need A Budget). These tools help users budget, track expenses, and achieve savings goals, showcasing the benefits of fintech services.
4. Investment Platforms for Everyone
- The democratization of investment is evident through platforms like Robinhood and Acorns, which lower the barriers for novice investors. With user-friendly interfaces and educational resources, these platforms encourage more individuals to participate in investing.
- The shift from traditional brokerage firms to mobile-first investment solutions highlights a growing trend toward user empowerment.
5. Blockchain and Cryptocurrencies
- Understanding fintech also involves recognizing the impact of blockchain technology and cryptocurrencies on the financial landscape. Cryptos such as Bitcoin and Ethereum have not only created new asset classes but have also catalyzed innovation in payment processing and contract management.
- Financial professionals must stay informed about the regulatory landscape surrounding blockchain to navigate potential compliance challenges.
6. Regulation and Compliance Innovations
- As the fintech landscape evolves, so too does the regulatory environment. Fintech companies are increasingly developing compliance solutions using technology to streamline regulations while ensuring consumer protection.
- Collaboration between regulators and fintech firms is essential to foster innovation while upholding financial stability and security.
7. Emphasis on Security and Data Privacy
- Given the sensitive nature of financial data, security has become a top priority in the fintech industry. Solutions employing advanced encryption, biometrics, and AI-driven fraud detection mechanisms are vital for building consumer trust.
- Fintech firms are heavily investing in secure technologies to protect user information against potential breaches, further highlighting the importance of cybersecurity in the growth of the sector.
8. Fintech Examples Leading the Charge
- Numerous companies exemplify these trends, illustrating how they adapt to changes in consumer expectations and technology:
| Company | Innovation Focus | Key Service |
|---|---|---|
| PayPal | Digital payment solutions | E-commerce payment platform |
| Revolut | Global banking without borders | Multi-currency accounts |
| Coinbase | Cryptocurrency exchange | Digital asset trading |
| TransferWise | International money transfers | Low-cost cross-border payments |
The fintech industry overview illustrates that technology is fundamentally reshaping financial services. By staying abreast of these key trends and insights, financial professionals can strategically navigate this dynamic landscape and help their clients leverage the most effective fintech solutions available.
Types of Fintech Solutions: Exploring Diverse Offerings
The fintech industry overview highlights an evolving landscape of innovative financial services powered by technology. Encompassing a range of products, each type of fintech solution serves unique needs within the financial ecosystem. Financial professionals such as accountants, advisors, and bankers must understand these solutions to navigate an increasingly digital financial world. Below are the primary types of fintech offerings, showcasing their diversity and relevance.
1. Payment Processing Solutions
Payment solutions have revolutionized how transactions occur. Key finance technologies facilitate secure and swift money transfers, both for businesses and consumers. Common types include:
- Mobile Wallets: Applications like Apple Pay and Google Wallet allow users to store payment information securely on their devices, enabling quick and convenient transactions.
- Payment Gateways: Services such as PayPal and Stripe provide merchants with a seamless means to process online payments safely.
2. Lending Platforms
Innovative lending solutions have disrupted traditional banking methods. They provide faster, more accessible financing options:
- Peer-to-Peer Lending: Platforms like LendingClub connect borrowers directly with individual investors, often resulting in lower interest rates.
- Alternative Credit Scoring: Technologies analyze non-traditional data (such as social media activity) to assess creditworthiness, opening opportunities for those with limited credit histories.
3. Investment Management Solutions
Fintech has crafted a new era for investment management, rendering it accessible for individuals and retail investors:
- Robo-Advisors: Automated services like Betterment or Wealthfront assess user risk tolerance and manage investment portfolios with minimal human intervention.
- Social Trading Platforms: These platforms, such as eToro, allow users to mirror the investment strategies of experienced traders, making participation in the market less intimidating.
4. Insurance Technology (Insurtech)
The insurtech sector employs technology to enhance insurance services, making them more user-friendly:
- On-Demand Insurance: Companies such as Slice offer flexible, usage-based insurance policies that adapt to consumers’ needs.
- Claims Automation: Technologies streamline the claims process through digital customer service and automated assessments, significantly reducing processing times.
5. Personal Finance Management Solutions
In a bid to assist individuals in tracking and managing their finances, these solutions emerge as indispensable tools:
- Budgeting Apps: Services like Mint or YNAB (You Need a Budget) help users categorize expenses, set budgets, and gain insights into their spending habits.
- Savings Apps: Solutions such as Acorns round up purchases to save small amounts, fostering a habit of saving without much conscious effort.
6. Cryptocurrency and Blockchain Solutions
Cryptocurrencies and their underlying blockchain technology represent a fundamental shift in financial transactions:
- Cryptocurrency Exchanges: Neobanks such as Coinbase or Binance facilitate buying, selling, and trading digital assets securely.
- Smart Contracts: These self-executing contracts on blockchain revolutionize transactions by automating processes and reducing reliance on intermediaries.
Comparison Table of Fintech Solutions
| Type of Fintech Solution | Key Examples | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Payment Processing | Apple Pay, Stripe | Quick transactions, Secure |
| Lending Platforms | LendingClub, Upstart | Accessible credit, Disruptive |
| Investment Management | Betterment, Robinhood | User-friendly, Automated |
| Insurtech | Lemonade, Root | Customizable, Efficient |
| Personal Finance | Mint, Digit | Insightful, User-centric |
| Cryptocurrency | Binance, Ethereum | Innovative, Decentralized |
Understanding these diverse types of fintech solutions equips financial professionals with the knowledge to enhance service offerings and address consumer needs. As the fintech industry evolves, staying informed about these innovations will be crucial for success and competitive advantage. Whether it involves streamlining payments, optimizing investment strategies, or facilitating insurance claims, each niche within the fintech sector has its implications for the future of financial services.
Understanding Fintech: The Technology Behind Financial Innovations
In a world increasingly reliant on technology, understanding fintech means delving into the innovative technology that underpins the financial services sector. This comprehensive examination encompasses a range of key technologies and innovations that are reshaping traditional financial practices, making processes more efficient, secure, and user-friendly. Below, professionals in the financial sector can explore the core elements facilitating the rise of fintech.
Key Technologies in Fintech
- Blockchain Technology
- Enables secure and transparent transactions.
- Acts as a decentralized ledger, significantly reducing fraud.
- Used in cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, and facilitates smart contracts.
- Blockchain Technology
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Powers machine learning algorithms for predictive analytics.
- Enhances customer service through chatbots and virtual assistants.
- Provides risk assessment and fraud detection capabilities.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Big Data Analytics
- Processes vast amounts of financial data to identify trends and make informed decisions.
- Empowers personalized banking experiences and targeted marketing.
- Aids in regulatory compliance by analyzing transactional data.
- Big Data Analytics
- Cloud Computing
- Offers scalable resources, allowing fintech companies to operate more efficiently.
- Facilitates advanced data storage and access from anywhere.
- Reduces IT costs and improves system integrations across platforms.
- Cloud Computing
- Application Programming Interfaces (APIs)
- Allows different software systems to communicate seamlessly.
- Commonly used in open banking, facilitating third-party services.
- Enables the creation of new fintech products and services by leveraging existing infrastructure.
- Application Programming Interfaces (APIs)
Innovations Changing Financial Services
- Mobile Wallets: Allow users to store and manage their payment information conveniently on mobile devices.
- Peer-to-Peer Lending Platforms: Enable individuals to lend money directly to each other, bypassing traditional banks.
- Robo-Advisors: Use algorithms to create and manage investment portfolios, democratizing wealth management.
- Insurtech Solutions: Innovate the insurance industry by automating claims processing and underwriting through technology.
Benefits of Technology in Fintech
- Enhanced Customer Experience
- Fast, intuitive interfaces improve user interaction with financial services.
- 24/7 availability of services through mobile apps and online platforms.
- Enhanced Customer Experience
- Cost Reduction
- Automating processes reduces the need for manual intervention, lowering operational costs.
- Efficient risk management tools prevent significant financial losses.
- Cost Reduction
- Increased Accessibility
- Technology facilitates access to financial services for underserved populations through mobile and online solutions.
- Micro-financing and alternative lending platforms are emerging from innovative technologies.
- Increased Accessibility
Summary of Key Technologies
| Technology | Functionality | Impact on Fintech |
|---|---|---|
| Blockchain | Decentralized transaction management | Reduces fraud and enhances trust |
| Artificial Intelligence | Machine learning and automation | Improves customer service and operational efficiency |
| Big Data Analytics | Data analysis for insights | Enables informed decision-making |
| Cloud Computing | Scalable resources and systems integration | Enhances operational flexibility |
| APIs | Facilitates interoperability between systems | Promotes innovation through shared services |
Professionals in the financial arena must keep abreast of these transformative technologies to harness their potential effectively. From driving efficiency to democratizing access, understanding fintech has never been more critical in today’s rapidly evolving financial landscape. As innovations continue to arise, the fintech industry’s future promises to be dynamic and fruitful for those willing to embrace the change.

Benefits of Fintech Services: Enhancing Efficiency and Accessibility
The fintech industry overview reveals a dynamic landscape driven by technology, making financial services more efficient and accessible than ever before. Through a variety of innovations, fintech solutions are transforming traditional banking and finance, offering both businesses and consumers distinct advantages. Below are key benefits of fintech services that highlight their transformative potential in the financial sector.
1. Improved Operational Efficiency
- Automation of Processes: Fintech eliminates redundancy and streamlines operations through automation. Processes such as loan approvals and account openings are expedited, which not only reduces human error but also enhances client satisfaction.
- Cost-Effective Solutions: By leveraging digital technologies, fintech companies minimize operational costs. Traditional banks often face high overheads, while fintech’s lean structures allow for reduced fees for customers.
2. Enhanced Customer Experience
- User-Friendly Platforms: Fintech solutions often incorporate intuitive design and user experience principles, making it easier for clients to navigate financial services.
- 24/7 Availability: Unlike conventional banking hours, fintech allows users to access services anytime and anywhere. This convenience addresses the needs of modern consumers who demand quick and easy access to their finances.
3. Increased Accessibility
- Substantial Scope for the Unbanked: Fintech bridges the gap for the unbanked and underbanked populations. Mobile wallets and peer-to-peer lending platforms provide financial access to individuals who previously lacked banking facilities.
- Global Reach: Fintech solutions can be accessed virtually anywhere, making them significant for cross-border transactions and enabling users in remote areas to participate in the global economy.
4. Personalized Financial Services
- Tailored Products: With advanced data analytics, fintech firms can offer personalized financial products and services suited to an individual’s specific needs and financial history.
- Robust Consumer Insights: Using artificial intelligence, fintech companies analyze user data to enhance recommendations, leading to better financial decision-making.
5. Integration of Innovative Technologies
- Blockchain Capabilities: Many fintech solutions are underpinned by blockchain technology, which significantly enhances security and transparency in transactions.
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: These technologies help to identify trends, manage risks more effectively, and personalize services, thereby improving overall service delivery.
6. Regulatory Compliance Support
- Simplified Compliance Processes: Advanced regulatory technology (RegTech) solutions allow fintech companies to remain compliant with ever-changing regulations more efficiently. This reduces the burden on institutions and improves financial integrity.
Key Takeaways Table
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Improved Operational Efficiency | Automation reduces errors and enhances speed. |
| Enhanced Customer Experience | User-friendly interfaces and availability lead to satisfaction. |
| Increased Accessibility | Access for unbanked populations and global reach. |
| Personalized Financial Services | Tailored offerings based on significant customer data. |
| Integration of Innovative Technologies | Blockchain and AI optimize security and service quality. |
| Regulatory Compliance Support | Helps maintain compliance efficiently and reduces risks. |
These multiple facets of fintech services not only enhance efficiency and accessibility but redefine customer engagement and service delivery in the financial sector. By understanding these crucial benefits, financial professionals can leverage fintech examples and applications to better serve their clients and adapt to ongoing industry changes. As technology continues to evolve, the significance of fintech in promoting inclusive financial practices is set to grow, providing even broader opportunities for all stakeholders involved.
Key Technologies Driving the Fintech Revolution
In the rapidly evolving fintech industry overview, technology serves as the backbone, facilitating innovation and reshaping traditional financial services. Various key technologies are driving this revolution, each contributing to a comprehensive change in how financial transactions and services are delivered. Understanding these key technologies provides a broader insight into fintech solutions, ultimately enhancing the financial ecosystem’s efficiency and accessibility.
1. Blockchain Technology
- Definition: Blockchain is a decentralized ledger technology that ensures transactions are transparent, secure, and irreversible.
- Benefits:
- Enhances security by providing a tamper-resistant structure.
- Reduces fraud and operational risks.
- Benefits:
- Applications:
- Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum leverage blockchain for secure transactions.
- Smart contracts automate agreements without intermediaries.
- Applications:
2. Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Definition: AI refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines that are programmed to think and learn.
- Benefits:
- Processing large data sets to uncover actionable insights.
- Enhancing customer service through chatbots and personalized banking experiences.
- Benefits:
- Applications:
- Fraud detection algorithms analyze patterns and identify anomalies.
- Robo-advisors provide tailored investment advice based on individual client profiles.
- Applications:
3. Big Data Analytics
- Definition: Big Data encompasses vast volumes of structured and unstructured data that can be analyzed for insights.
- Benefits:
- Enables financial institutions to make informed decisions based on consumer behavior.
- Segments customers for targeted marketing and product development.
- Benefits:
- Applications:
- Risk assessment models leverage historical data to predict potential loan defaults.
- Credit scoring utilizes diverse data points for more accurate evaluations.
- Applications:
4. Cloud Computing
- Definition: Cloud computing allows for the storage and processing of data over the internet rather than local servers.
- Benefits:
- Provides scalability and flexibility in resource management.
- Reduces operational costs for financial institutions.
- Benefits:
- Applications:
- Online banking services facilitate access to financial information anytime, anywhere.
- Fintech startups use cloud infrastructure to quickly launch and iterate on products.
- Applications:
5. Mobile Technology
- Definition: Mobile technology encompasses devices and applications that enable financial transactions and services on-the-go.
- Benefits:
- Increases user engagement through mobile-friendly interfaces.
- Promotes financial inclusion by making services accessible to underbanked populations.
- Benefits:
- Applications:
- Mobile wallets such as Apple Pay and Google Wallet accelerate payment processes.
- Peer-to-peer lending apps connect borrowers and lenders directly through mobile platforms.
- Applications:
6. Internet of Things (IoT)
- Definition: IoT refers to interconnected devices that communicate and share data between each other and with central systems.
- Benefits:
- Provides real-time data monitoring and analytics.
- Enhances customer experiences through instant service adjustments.
- Benefits:
- Applications:
- Smart ATMs offer tailored services based on user data.
- Wearable devices with payment capabilities streamline in-store transactions.
- Applications:
Summary of Technologies
| Technology | Key Features | Major Benefits | Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Blockchain | Decentralization, security | Fraud reduction, transparency | Cryptocurrencies, smart contracts |
| Artificial Intelligence | Machine learning, natural language processing | Personalized service, risk assessment | Chatbots, robo-advisors |
| Big Data Analytics | Data mining, predictive modeling | Informed decision-making, targeted marketing | Credit scoring, risk assessment |
| Cloud Computing | Scalability, remote access | Cost reduction, enhanced collaboration | Online banking, SaaS fintech applications |
| Mobile Technology | Accessibility, real-time engagement | Increased convenience, financial inclusion | Mobile wallets, peer-to-peer lending |
| Internet of Things | Device interconnectivity, real-time data | Instant service adjustments, enhanced customer experience | Smart ATMs, payment-enabled wearables |
By leveraging these transformative technologies, the fintech industry is not only enhancing existing services but also creating innovative solutions that cater to the evolving needs of consumers and businesses alike. As financial professionals analyze this landscape, understanding these key technologies is crucial for capitalizing on emerging opportunities and navigating the complexities of the fintech revolution.
What is Fintech in Practice? Real-World Applications
Fintech, short for financial technology, has swiftly become one of the most transformative sectors within the broader financial industry. Its influence stretches far and wide, impacting consumers and businesses alike. By exploring fintech industry overview, this section divulges the thought-provoking what is fintech definition while also illustrating its practical applications through real-world examples. Here, the examination focuses on how different solutions are redefining traditional financial services.
A Deep Dive into Real-World Applications
- Digital Payments and Mobile Wallets
- Companies like PayPal and Venmo have revolutionized the way money is transferred. These platforms facilitate instant fund transfers between users and businesses, proving to be more efficient and user-friendly than traditional banking methods.
- Digital Payments and Mobile Wallets
- P2P Lending
- Platforms such as LendingClub and Prosper allow individuals to lend and borrow money directly from one another, bypassing traditional banking institutions. This model not only lowers costs but also broadens access to credit for individuals who may be underserved by traditional banks.
- P2P Lending
- Robo-Advisors
- Firms like Betterment and Wealthfront use algorithms and AI to provide personalized investment advice. By analyzing markets and individual user preferences, these robo-advisors can manage investment portfolios efficiently at much lower fees than conventional financial advisors.
- Robo-Advisors
- Insurtech
- Technological innovations in insurance, known as insurtech, manifest in companies like Lemonade, which leverages AI to underwrite policies and make claims processing faster and more transparent—greatly enhancing customer experience.
- Insurtech
- Blockchain and Cryptocurrency
- Firms like Coinbase and Binance exemplify how blockchain technology disrupts the traditional banking model by providing decentralized finance (DeFi) services and allowing users to trade cryptocurrencies seamlessly across the globe.
- Blockchain and Cryptocurrency
- Alternative Credit Scoring
- Companies such as ZestFinance utilize machine learning techniques to assess creditworthiness based on a broader range of data points. This strategy democratizes access to credit for underserved populations who may not have traditional credit scores.
- Alternative Credit Scoring
- Financial Education Tools
- Platforms like Khan Academy and SmartAsset provide users with resources to improve their financial literacy. By making knowledge accessible, these tools empower consumers to make informed financial decisions.
- Financial Education Tools
Illustrating the Fintech Landscape
| Application Type | Key Players | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Digital Payments | PayPal, Venmo | Instant fund transfers that are user-friendly and accessible. |
| P2P Lending | LendingClub, Prosper | Direct transactions between individuals, minimizing costs. |
| Robo-Advisors | Betterment, Wealthfront | Automated investment management using algorithms. |
| Insurtech | Lemonade | Fast, AI-driven underwriting processes in insurance. |
| Blockchain/Cryptocurrency | Coinbase, Binance | Decentralized trading platforms for cryptocurrencies. |
| Alternative Credit Scoring | ZestFinance | Broader credit assessments utilizing machine learning. |
| Financial Education Tools | Khan Academy, SmartAsset | Resources for improving financial literacy. |
The Broad Impact of Fintech Solutions
The transformative nature of fintech solutions allows financial professionals, like accountants and bankers, to rethink the way they interact with clients. With fintech examples and applications, professionals can leverage these innovations to provide better services, improve customer satisfaction, and enhance efficiency.
Understanding these practical applications provides critical insight into how fintech services can significantly redefine business operations, reduce costs, and foster greater financial inclusion across the global population. As the sector continues to evolve, finance professionals must stay updated to remain relevant in this rapidly changing landscape.
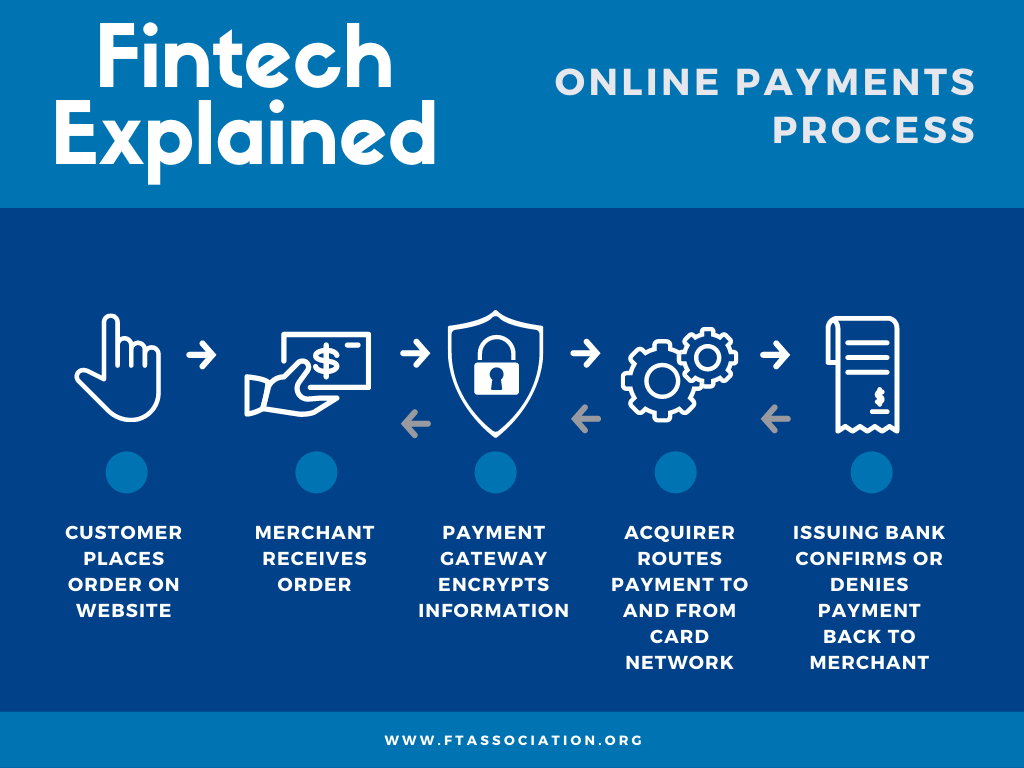
Fintech Examples: Companies Leading the Change
The fintech industry overview showcases a plethora of companies that are embracing financial technology to revolutionize the traditional financial landscape. These organizations are pushing the boundaries of innovation, offering diverse solutions to meet the needs of consumers and businesses alike. Below are some noteworthy examples of companies that are effectively leading the charge in the fintech sector:
- PayPal: One of the pioneers in digital payments, PayPal has transformed how money is transferred online. The platform allows users to send payments and receive funds seamlessly. With enhanced features like PayPal Credit and integration with various e-commerce platforms, it simplifies transactions for users and merchants.
- Square: Founded by Twitter’s Jack Dorsey, Square has redefined the point-of-sale experience with its easy-to-use mobile payment solutions. Its suite of services includes payment processing, inventory management, and even small business loans. This comprehensive approach supports businesses of all sizes, making it an essential player in understanding fintech.
- Stripe: Specializing in online payment processing, Stripe enables businesses to accept payments in various currencies with minimal hassle. Beyond simple payment processing, they provide tools for billing, fraud prevention, and even global payments, ensuring businesses can operate without boundaries.
- Robinhood: Aiming to democratize finance, Robinhood is a commission-free trading platform that allows users to invest in stocks, ETFs, and cryptocurrencies without paying traditional brokerage fees. This has expanded market access, especially for younger generations that may not have previously participated in trading.
- Ant Financial: An offshoot of Alibaba Group, Ant Financial offers a range of services, including Alipay, a mobile payment platform. It also focuses on enabling small businesses and individual users to access micro-lending services, insurance, and investment options, driving a significant impact in the fintech space.
- Braintree: As a subsidiary of PayPal, Braintree specializes in mobile payments and offers businesses tools to accept payments through mobile applications. The platform supports various payment methods, including credit cards and digital wallets, highlighting the importance of adaptability in the types of fintech solutions.
- N26: Based in Europe, N26 is a digital bank offering hassle-free banking services via mobile apps. With a focus on transparency, N26 provides features like real-time notifications, fee-free international transactions, and simple account management, demonstrating how technology can improve the customer experience in the banking realm.
The prominent companies listed above serve as examples of how fintech services are transforming the financial industry. They are leaders not only in adopting advanced technologies but also in providing solutions that enhance customer accessibility and satisfaction.
Key Table of Fintech Examples
| Company | Primary Offering | Notable Features |
|---|---|---|
| PayPal | Digital Payments | Instant transfers, Buyer Protection |
| Square | Point-of-Sale Solutions | Mobile payments, Inventory management |
| Stripe | Payment Processing | Multi-currency support, Fraud prevention |
| Robinhood | Stock Trading | Commission-free trades, Cryptocurrency |
| Ant Financial | Mobile Payment and Financial Services | Micro-loans, Insurance options |
| Braintree | Mobile Payment Solutions | Various payment methods, Seamless integration |
| N26 | Digital Banking | Real-time notifications, No foreign transaction fees |
Each of these companies exemplifies the ongoing fintech innovations that are creating a more accessible, efficient, and user-friendly financial ecosystem. They illustrate the rapid changes taking place in the financial landscape, powered by technology. As professionals in finance continue to explore these advancements, it’s crucial to stay informed about the latest developments and leverage these solutions for improved client service. Understanding who is leading the change can provide valuable insights into the future of finance.
The Role of Blockchain in Fintech Innovations
Blockchain technology has emerged as a formidable force in the fintech industry overview, offering groundbreaking ways to enhance financial processes. This decentralized ledger ensures transparency, security, and efficiency, making it a vital part of numerous fintech solutions. As financial professionals seek to understand the implications of blockchain, it is essential to explore how it reshapes financial services and transactions.
Key Aspects of Blockchain in Fintech:
- Decentralization: Traditional financial systems often rely on centralized control, which can lead to inefficiencies and vulnerabilities. Blockchain disrupts this model by allowing multiple parties to access the same information, reducing the risk of fraud and increasing trust.
- Immutability: Once data is recorded on a blockchain, it cannot be altered without consensus from all parties involved. This characteristic ensures the integrity of transactional data, making it highly reliable for financial applications.
- Smart Contracts: These self-executing contracts facilitate automatic execution of agreements once predetermined conditions are met. Financial professionals can leverage smart contracts to streamline processes such as loan approvals and trade settlements, minimizing the need for intermediaries.
- Cost Efficiency: By eliminating intermediaries and reducing transactional overheads, blockchain technology can significantly lower operational costs. Financial institutions can pass these savings onto clients, enhancing competitive positioning within the fintech landscape.
- Increased Security: Blockchain employs cryptographic techniques that ensure the confidentiality and security of transactions. This robust security framework helps mitigate risks associated with cyber threats, which are particularly pertinent in the fintech solutions space.
Comparison of Blockchain vs. Traditional Financial Systems:
| Feature | Blockchain Technology | Traditional Financial Systems |
|---|---|---|
| Control | Decentralized | Centralized |
| Data Integrity | Immutable | Subject to errors and fraud |
| Execution Speed | Real-time or near real-time | Often delayed |
| Security Levels | High (cryptographic methods) | Moderate (mostly dependent on firewall and protocols) |
| Transaction Costs | Lower (fewer intermediaries) | Higher (multiple intermediaries) |
Key Innovations Enabling Blockchain in Fintech:
- Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT): Underpinning blockchain, DLT enables the secure sharing of transaction records across multiple platforms, enhancing operational visibility.
- Tokenization: This process involves converting assets into digital tokens on a blockchain, enabling fractional ownership and increased liquidity.
- Cross-Border Payments: Blockchain simplifies international transactions by reducing the need for currency conversion and minimizing intermediary bank fees.
Real-World Applications of Blockchain in Fintech:
- Cryptocurrencies: Bitcoin and Ethereum exemplify how blockchain can transform monetary systems, offering alternatives to traditional currencies.
- Supply Chain Finance: Blockchain aids in ensuring traceability of goods, enhancing trust in financial transactions related to supply chains.
- KYC Processes: Know Your Customer (KYC) requirements are streamlined using blockchain, as it provides a shared, verified record of customer identities across institutions.
In summary, understanding fintech innovations necessitates a close examination of how blockchain technologies are redefining the financial services landscape. By embracing these fintech examples, financial professionals can better navigate challenges, leverage opportunities, and position their organizations at the forefront of the digital revolution in finance.
How Artificial Intelligence is Transforming Fintech
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has emerged as a transformative force in the financial technology sector, revolutionizing how businesses operate, manage risk, and interact with customers. By harnessing the power of machine learning algorithms, predictive analytics, and natural language processing, the Fintech industry overview is expanding rapidly, providing innovative solutions that enhance financial services.
Here are some of the key areas in which AI is making a significant impact:
- Fraud Detection and Prevention: AI systems continuously analyze transaction patterns to identify anomalies that could indicate fraudulent activity. By recognizing unusual behavior in real time, financial institutions can prevent fraudulent transactions before they occur.
- Risk Assessment: Traditional methods of evaluating creditworthiness often fall short in today’s fast-paced environment. AI tools analyze a broader spectrum of data points—such as social media activity, transaction history, and behavioral patterns—allowing for more accurate risk assessments.
- Customer Service Automation: Chatbots powered by AI provide immediate customer support and handle routine inquiries, allowing financial institutions to enhance user experience while significantly reducing operational costs. These virtual assistants are available 24/7, ensuring customers receive assistance whenever needed.
- Personalized Financial Services: With AI, companies can offer tailored services that meet individual customer needs. Algorithms can analyze a customer’s spending behaviors and financial goals to provide customized financial advice and product recommendations.
- Regulatory Compliance: As regulations become more complex, AI helps financial institutions navigate compliance requirements efficiently. AI systems can assist in monitoring transactions and flagging non-compliant activities without overwhelming compliance teams.
Key Technologies Integrating AI in Fintech
| Technology | Function | Impact on Fintech |
|---|---|---|
| Machine Learning | Analyzes large datasets to derive insights | Improves risk assessment and fraud detection |
| Natural Language Processing | Understands customer inquiries in real-time | Enhances customer service through effective chatbots |
| Predictive Analytics | Provokes foresight by predicting market trends | Guides financial decisions and investment strategies |
| RPA (Robotic Process Automation) | Automates repetitive tasks | Streamlines operations and reduces manual errors |
Benefits of AI in Fintech Services
The adoption of AI in the fintech industry overview has several compelling benefits, including:
- Increased Efficiency: AI systems automate mundane tasks, allowing professionals to focus on more value-adding activities.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: AI provides data-driven insights that support informed decision-making processes.
- Cost Reduction: By minimizing human errors and decreasing labor costs through automation, AI helps firms reduce operational expenses.
- Stronger Customer Relationships: Automated personalization fosters customer loyalty by making clients feel valued and understood.
- Data Security: AI algorithms enhance data protection, analyzing threats in real time to safeguard sensitive customer information.
As the understanding of fintech deepens, financial professionals must embrace these innovations to remain competitive. The integration of AI in the finance sector is not merely a trend but a paradigm shift that is reshaping the industry’s landscape. By leveraging these technologies, businesses will not only improve their operational processes but will also enhance the customer experience, solidifying their position in a rapidly evolving marketplace.

The Impact of Mobile Technology on the Fintech Landscape
Mobile technology has dramatically reshaped the fintech industry overview, influencing how financial services are delivered and consumed. The proliferation of smartphones and mobile applications has made financial transactions more accessible, efficient, and user-friendly. The following points illustrate the transformative role of mobile technology in the Fintech ecosystems:
- Increased Accessibility: Mobile devices have democratized access to financial services. In regions with limited banking infrastructure, mobile technology allows users to conduct transactions, manage accounts, and engage with financial institutions without requiring physical branches. This has significantly increased the number of unbanked and underbanked individuals who can now participate in the financial system.
- Enhanced User Experience: The rise of user-centric design in mobile applications has reshaped how Clients interact with their financial services. Intuitive interfaces, streamlined processes, and enhanced functionalities improve the overall customer experience. Fintech solutions, such as mobile payment apps and digital banking platforms, prioritize user experience, leading to higher satisfaction and loyalty.
- Real-Time Transactions: Mobile technology facilitates instantaneous transactions, enabling users to send and receive money in real-time. This immediacy benefits consumers and businesses, allowing for quicker payments and reducing cash flow issues for small enterprises. As per studies, real-time payment systems have resulted in dramatically improved operational efficiencies for many companies.
- Innovative Payment Methods: The explosion of mobile wallets, contactless payments, and peer-to-peer transfer systems exemplifies the influx of innovation fueled by mobile technology. Through apps like Venmo, PayPal, and Apple Pay, users can perform seamless transactions with just a few taps on their screens. These innovations cater to consumer demand for convenience and speed, reshaping the payments landscape.
- Integration of AI and Machine Learning: Mobile technology often works alongside Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning systems, significantly enhancing functionalities. Personal finance apps use algorithms to analyze spending habits, suggest saving strategies, and provide tailored financial advice to users. This convergence of technologies further enriches the understanding fintech paradigm, showcasing how they complement and enhance each other.
- Increased Security Measures: As mobile technology advances, so do security protocols to protect sensitive financial data. Biometric authentication methods, such as fingerprint and facial recognition, have been integrated into mobile financial applications, enhancing security and reducing fraud risks. These advances ensure that users can transact confidently, contributing to the overall trust in fintech solutions.
- Regulatory Compliance through Mobile Solutions: Mobile technology enables fintech companies to remain compliant with financial regulations efficiently. By utilizing cloud-based services and automated reporting tools, firms can ensure they meet the evolving regulatory landscape without overwhelming their operational capabilities.
Table: Key Mobile Technology Trends in Fintech
| Trend | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Mobile Payments | Rise in mobile wallet usage and contactless payments | Enhanced convenience for consumers |
| Real-Time Banking | Instant fund transfers and payments | Improved cash flow management for businesses |
| AI-Powered Services | Personalized financial advice via mobile applications | Tailored user experience, driving customer loyalty |
| Enhanced Security | Advanced biometric authentication | Increased user trust and safety |
| Regulatory Adaptations | Cloud solutions for regulatory compliance | Streamlined compliance processes |
Through these focal points, the impact of mobile technology on the fintech landscape becomes clear; it not only improves access and user experience but also drives innovation and security in financial services. This distinctly illustrates the broader implications of mobile technology within the fintech examples and applications, showcasing its importance in the current financial ecosystem. As industry professionals, understanding these dynamics is crucial for staying ahead in a rapidly evolving marketplace.
Regulatory Challenges in the Fintech Industry
In the dynamic landscape of the fintech industry, professionals must navigate a complex web of regulatory challenges that can impact operations, innovation, and customer trust. As financial technology continues to evolve, the regulatory environment is struggling to keep pace. Here, we will explore several key regulatory challenges that the fintech sector faces today.
1. Diverse Regulatory Frameworks
- Global Variation: Fintech operates on a global scale, but regulatory standards vary significantly from one country to another. This disparity can hinder operations for financial professionals who wish to expand internationally. Companies often face difficulties in complying with various local laws and regulations, which can lead to increased compliance costs and operational inefficiencies.
- Sector-Specific Regulations: Beyond geographical differences, fintech companies also have to contend with sector-specific regulations that affect their operations. For instance, regulations governing payments, lending, and investments are distinct and can complicate the compliance landscape.
2. Data Privacy and Security Laws
- GDPR and Beyond: In Europe, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) has established stringent rules regarding how companies handle personal data. For fintech companies, ensuring compliance with data protection laws is crucial as they deal with sensitive financial information.
- Customer Trust: Failure to comply with data protection regulations can lead to severe financial penalties and can severely damage customer trust—an essential currency for fintech firms.
3. Risk Management and Fraud Prevention
- Heightened Scrutiny: As fintech companies involve themselves in innovative financial solutions, regulatory bodies focus on their risk management processes. Stakeholders must demonstrate their capability to handle emerging threats such as cyber attacks, money laundering, and fraud.
- Compliance Costs: Increased scrutiny often requires the implementation of more sophisticated compliance programs, which can be financially burdensome for startups and smaller companies in the fintech sector.
4. Licensing and Registration Requirements
- Evolving Criteria: Many fintech companies need to secure a license to operate in financial segments such as digital banking and investment services. The criteria for obtaining these licenses can shift, adding an additional layer of complexity to the regulatory process.
- Time Consumption: The licensing process can be both lengthy and costly, often hindering the speed at which new innovations reach the market.
5. Consumer Protection Regulations
- Balancing Act: Striking a balance between fostering innovation and protecting consumers is a significant challenge. Fintech professionals must ensure that their products are not only compliant with laws but also adhere to ethical standards in consumer treatment.
- Reputation Risks: Non-compliance with consumer protection regulations not only incites legal ramifications but can also harm a company’s reputation in an industry that thrives on trust and reliability.
Comparison Table: Regulatory Challenges Faced by Fintech Firms
| Regulatory Challenge | Impact on Fintech Firms | Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Diverse Regulatory Frameworks | Compliance costs, operational delays | Develop global compliance strategies |
| Data Privacy and Security Laws | Financial penalties, loss of customer trust | Invest in robust data protection and security protocols |
| Risk Management and Fraud Prevention | Increased surveillance, potential fines | Implement advanced risk management systems |
| Licensing and Registration Requirements | Delays in market entry, significant costs | Engage regulatory advisors for streamlined processes |
| Consumer Protection Regulations | Legal repercussions, reputation damage | Develop ethical frameworks and transparent customer policies |
In summary, navigating the regulatory challenges in the fintech industry requires a keen understanding of both local and global regulations. Financial professionals must proactively adapt and implement compliance strategies while maintaining an innovative edge. By remaining informed and strategic, fintech firms can better position themselves to thrive despite the regulatory hurdles they encounter. The fintech revolution marches on, but its road is undoubtedly paved with challenges that will shape its future in profound ways.
Future Trends in Fintech: What Lies Ahead?
The fintech industry overview provides a fascinating glimpse into the ongoing transformation of financial services, driven by technological advancements and changing consumer behaviors. As financial professionals adapt to the evolving landscape, it becomes crucial to understand emerging trends that are shaping the future of this dynamic sector. Below are some predictions and trends expected to shape the marketplace in the coming years.
1. Increased Adoption of Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Enhanced Decision-Making: Professionals in finance can anticipate a greater reliance on AI for data analysis. The technology’s ability to process massive amounts of data will lead to more accurate predictions and improved decision-making.
- Personalized Services: AI will enable the creation of tailored financial products and services to meet the unique needs of clients.
2. Rise of Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
- Peer-to-Peer Transactions: DeFi is set to revolutionize traditional finance by reducing reliance on intermediaries, thereby enhancing efficiency and transparency.
- Smart Contracts: Automated contracts built on blockchain will minimize the need for manual oversight in transactions, streamlining processes.
3. Regulatory Innovations
- Adaptive Compliance: As the fintech industry overview evolves, so will regulations. Financial professionals must stay informed on new compliance requirements as regulators aim to protect consumers while fostering innovation.
- RegTech Solutions: The integration of regulatory technology will assist institutions in adhering to regulatory frameworks efficiently and effectively.
4. Embedded Finance
- Seamless Transactions: Financial services will become increasingly integrated into non-financial platforms, allowing customers to access products with minimal friction.
- Wider Accessibility: This trend will enhance financial inclusion, making services accessible to underserved populations.
5. Sustainability in Fintech
- Green Finance Ventures: The sector will likely see a rise in sustainable investment solutions as environmental concerns take center stage. Financial professionals will increasingly be called upon to advise clients on eco-friendly investment options.
- Energy-efficient Blockchain: Innovations aimed at reducing the carbon footprint of blockchain technologies will become a priority.
6. Digital Currency and Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs)
- National Digital Currencies: Governments worldwide are exploring CBDCs, which may change the conventional banking framework and payment systems.
- Cryptocurrency Integration: The acceptance of digital currencies as legitimate payment methods will grow, offering new opportunities for investors and everyday users alike.
| Trend | Description | Implications for Financial Professionals |
|---|---|---|
| Increased Adoption of AI | Utilizing AI for enhanced data analysis and services | Need for upskilling in AI technologies |
| Rise of Decentralized Finance (DeFi) | Facilitating peer-to-peer transactions | Understanding DeFi products and risks |
| Regulatory Innovations | Evolution of compliance technology | Adapting to new regulatory landscapes |
| Embedded Finance | Integration of financial services into various platforms | Navigating partnerships with tech firms |
| Sustainability in Fintech | Emphasis on eco-friendly investment | Advising clients on green financial options |
| Digital Currency and CBDCs | Introduction of national digital currencies | Exploring new avenues in investment advice |
7. Enhanced Cybersecurity Measures
- Protecting Customer Data: As fintech expands, the threat landscape will evolve. Financial professionals must prioritize cybersecurity to protect sensitive information.
- Blockchain Security: Leveraging blockchain’s inherent security features will become a vital strategy in countering emerging cyber threats.
In summary, the future of fintech is not limited to technological innovations but extends into regulatory, ethical, and social realms as well. By keeping an eye on these trends, financial professionals can effectively navigate the changing landscape and seize emerging opportunities while preparing for challenges that lie ahead. Understanding fintech’s evolving nature will be imperative in adopting innovative solutions that continue to benefit consumers in a rapidly changing world.
Understanding Fintech: A Look at Customer Experience
In the fast-evolving world of finance, understanding fintech is becoming increasingly important, especially when it comes to customer experience. Fintech companies leverage technology to streamline financial services, aiming to enhance user interactions and satisfaction. A remarkable customer experience is essential for the growth and sustainability of fintech solutions. Below are key aspects that contribute to more engaging and effective customer experiences in the fintech industry.
1. Personalization
- Tailored Solutions: Fintech solutions use data analytics to provide personalized offerings. By analyzing customer behavior and preferences, fintech firms can tailor services ranging from investment advice to loan offers.
- User-Centric Interfaces: Intuitive designs are crucial. A well-structured user interface minimizes complexity and allows customers to navigate services smoothly.
2. Seamless Onboarding
- Rapid Account Creation: The onboarding process is often a customer’s first interaction with a fintech service. Fintechs streamline this by offering online applications that require minimal documentation, reducing friction and enhancing satisfaction.
- Instant Verification: Many fintech platforms implement biometric verification or AI algorithms for identity checks, allowing users to access services without waiting days for approvals.
3. Accessibility
- 24/7 Availability: Unlike traditional banks with limited hours, most fintech services offer round-the-clock access. Customers can perform transactions, make inquiries, and receive support anytime.
- Multi-Device Compatibility: Many applications are designed for a range of devices, ensuring a consistent experience from smartphones to desktop computers.
4. Enhanced Communication
- Omni-channel Support: Providing support across various channels—chatbots, live chat, email, or phone—is vital for an excellent customer experience. Fintech firms that integrate responsive customer service can quickly address user concerns.
- Proactive Engagement: Use of AI helps fintech companies anticipate customer needs, allowing them to initiate contact for relevant services or updates.
5. Security Concerns
- Trust in Technology: Security features like two-factor authentication and secure encryption are essential to boost customer confidence. A clear communication strategy regarding data protection measures can significantly enhance the user experience.
- Transparent Policies: Fintech companies that openly communicate their security policies and practices foster trust and mitigate fears regarding personal data misuse.
6. Continuous Feedback and Improvement
- User Surveys: Fintechs often use surveys to gather insights on customer experiences. This real-time feedback allows for quick adjustments to services, making necessary improvements.
- Iterative Design: Many successful fintechs engage in continuous iterations based on user feedback, enhancing the overall usability and experience of their platforms.
Overview of Customer Experience Characteristics
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Personalization | Tailored offerings based on user data |
| Seamless Onboarding | Quick and efficient account setup |
| Accessibility | 24/7 service availability across devices |
| Enhanced Communication | Support through multiple channels |
| Security Concerns | Trust-building through robust security measures |
| Continuous Feedback | Ongoing improvements based on customer insights |
In summary, understanding fintech is vital for financial professionals who seek to enhance customer experiences. The importance of personalized offerings, seamless onboarding processes, and robust security measures cannot be overstated. By focusing on these key areas and employing technology effectively, fintech firms can not only meet but exceed customer expectations, thus securing loyalty and fostering long-term relationships in an increasingly competitive market.
Fintech’s Role in Promoting Financial Inclusion
The fintech industry overview highlights an essential aspect of this rapidly evolving sector: promoting financial inclusion. Financial inclusion refers to the accessibility of financial services to underserved populations, including those without traditional banking access. Understanding fintech in the context of financial inclusion reveals how technologies are breaking down barriers and creating opportunities for individuals and businesses alike.
Transformative Financial Solutions
Fintech solutions have significantly contributed to advancing financial inclusion by offering various technologies and services that target the unbanked and underbanked populations. Here are some vital players in this movement:
- Mobile Banking: Utilization of smartphones enables users to access banking services anywhere, ensuring that geographical barriers are eliminated.
- Microfinance Platforms: They offer small loans and financial services tailored for individuals who lack access to traditional banking.
- Digital Payment Systems: Users can transact efficiently without the need for a conventional bank account, paving the way for those who may not trust traditional banking systems.
- Cryptocurrency Services: Digital currencies facilitate borderless transactions and empower users in regions with unstable economies.
Key Benefits of Fintech for Financial Inclusion
The benefits of fintech services in promoting financial inclusion demonstrate a paradigm shift in how financial services are perceived and accessed. Here are several ways fintech is driving this change:
- Lower Costs: Fintech firms typically operate with lower overhead costs compared to traditional banks, allowing them to offer more affordable services. This cost-effectiveness is especially crucial for low-income individuals.
- User-Friendly Interfaces: Many fintech applications prioritize user experience, making it easier for individuals with limited financial literacy to navigate and utilize financial services effectively.
- Increased Accessibility: With the growing prevalence of smartphones and internet access, fintech solutions are increasingly reachable. Even in remote areas, users can obtain financial services through mobile apps, enhancing accessibility.
- Empowerment through Education: Fintech companies often integrate personal finance education within their platforms, empowering individuals to make informed financial decisions and promoting better financial habits.
Case Studies and Impact
Several case studies illustrate the tangible impact of fintech on financial inclusion:
- M-Pesa (Kenya): This mobile money transfer and payment service enables millions of Kenyans to carry out financial transactions without a traditional bank account. The platform has transformed how individuals receive salaries, send money, and conduct business.
- Kiva: By providing an online platform for micro-lending, Kiva connects lenders from across the globe with low-income entrepreneurs. This approach fosters entrepreneurship while ensuring financial support reaches those who need it the most.
Future Prospects
The increasing role of fintech in promoting financial inclusion suggests a promising future. As technology evolves, the potential for scalability and reaching even more underserved demographics grows. Emerging markets are likely to witness an uptick in innovative solutions aimed at integrating unbanked individuals into the financial system.
Fintech’s ability to harness data analytics and artificial intelligence enables personalized financial products that cater specifically to the needs of diverse user bases. This tailored approach will likely contribute to sustained economic growth and empower individuals to participate fully in the financial ecosystem.
By supporting and further advancing understanding fintech, financial professionals can grasp the significance of these developments and leverage them for broader financial inclusion initiatives. The fintech examples and applications in this sphere demonstrate that technology can indeed be a powerful ally in the quest for economic equality.
Case Studies: Successful Fintech Implementations
In an era marked by swift technological advancements, the fintech industry overview offers a fascinating glimpse into successful implementations that have reshaped financial services. Across the globe, various companies have successfully harnessed technological innovations to offer improved financial solutions, enhancing both customer experiences and operational efficiencies.
Here are several noteworthy case studies that illustrate successful fintech solutions across different verticals of the financial services sector:
1. Revolut: Disrupting Banking Norms
- Overview: Founded in 2015, Revolut is a prominent fintech that offers services ranging from currency exchange to cryptocurrency trading. Its mission is to create a one-stop banking platform for users around the world.
- Successful Implementation:
- Multi-Currency Accounts: Users can hold, exchange, and transfer currencies seamlessly, making international travel and commerce more accessible.
- Cryptocurrency Trading: Allowing customers to buy and sell cryptocurrencies has attracted a tech-savvy audience looking for new investment opportunities.
- Successful Implementation:
2. Square: Revolutionizing Payment Processing
- Overview: Founded by Jack Dorsey, Square provides financial and merchant services via a mobile payment platform, which has become a staple for small to medium-sized businesses.
- Successful Implementation:
- Point-of-Sale Systems: Square’s easy-to-use card readers and software have enabled thousands of small businesses to accept card payments.
- Square Capital: Offering quick access to business loans enhances financial accessibility for merchants struggling with cash flow.
- Successful Implementation:
3. TransferWise (now Wise): Transparent Currency Transfers
- Overview: Established in 2011, Wise addresses the inherent challenges of currency exchange fees, positioning itself as a leader in the international money transfer scene.
- Successful Implementation:
- Real Exchange Rates: By using the mid-market rate without hidden charges, Wise promotes transparency and builds customer trust.
- Global Reach: The platform allows users to send money to over 70 countries, catering to a diverse clientele.
- Successful Implementation:
| Case Study | Key Offerings | Unique Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Revolut | Multi-currency accounts, crypto trading | Unified banking, instant transactions |
| Square | POS systems, Square Capital | Easy payment processing, loans for SMBs |
| TransferWise | Low-cost international transfers | Transparent pricing, fast services |
4. Robinhood: Democratizing Investing
- Overview: Launched in 2013, Robinhood emerged with the goal of making investing accessible to everyone by eliminating trading fees.
- Successful Implementation:
- User-Friendly Interface: The mobile app and website offer users a straightforward platform to buy and sell stocks and ETFs without waiting for traditional broker response times.
- Fractional Shares: Users can invest in high-priced stocks with as little as a dollar, enhancing accessibility for a broader audience.
- Successful Implementation:
5. Nubank: Breaking Barriers in Brazil
- Overview: Nubank operates primarily in Brazil and has become one of the largest fintechs in the world by challenging traditional banking with its digital-only solutions.
- Successful Implementation:
- No Fees: By offering zero-fee services, Nubank targeted underbanked customers unhappy with conventional banks.
- Customer-Centric Approach: A focus on customer service and satisfaction has helped build a loyal user base.
- Successful Implementation:
Summary
These case studies exemplify how diverse fintech innovations can successfully enhance financial services within global markets. Each company not only found solutions that catered to specific needs but also created an adaptable business model rooted in improving customer experiences. As the fintech industry overview evolves, observing these successful implementations can inspire financial professionals to explore new methodologies and technologies within their own practices.

Frequently Asked Questions
What is fintech and how does it differ from traditional banking?
Fintech, short for financial technology, refers to the integration of technology into offerings by financial services companies to enhance their use of financial services. Unlike traditional banking, which mainly relies on established protocols and physical locations, fintech utilizes advanced technologies such as mobile apps, blockchain, and artificial intelligence to streamline and innovate financial services, making them more accessible, efficient, and user-friendly.
What are some key technologies driving fintech innovations?
Key technologies driving fintech innovations include blockchain, which facilitates secure and transparent transactions; artificial intelligence, which enables personalized financial services through data analysis; and machine learning, allowing for improved fraud detection and risk assessment. Additionally, mobile technology plays a crucial role, ensuring that financial services are easily accessible via smartphones, thus democratizing financial inclusion for users globally.
How do fintech companies improve customer experience in financial services?
Fintech companies enhance customer experience by leveraging technology to provide seamless, efficient, and personalized services. Features such as mobile banking applications allow users to manage their finances anytime, anywhere, while AI-driven chatbots offer instantaneous customer support. Moreover, fintech platforms often prioritize user-friendly interfaces and quick transaction processes, creating a more intuitive experience that contrasts sharply with the often cumbersome procedures found in traditional banks.
What is the impact of fintech on financial inclusion?
Fintech has a significant impact on financial inclusion as it provides underserved populations with access to essential financial services. By utilizing mobile technology and digital platforms, fintech solutions can offer banking services to those lacking access to traditional banking institutions. This includes microloans, digital wallets, and peer-to-peer lending, which empower individuals and small businesses, fostering greater economic participation and enabling them to improve their financial health.

























