Heart disease was listed as the cause of death for actor Gene Hackman, with his wife’s passing from hantavirus, a rodent-borne illness, being a contributing factor. The tragic incident unfolded in their Santa Fe, New Mexico home, raising concerns about the dangers of hantavirus and its potential impact on human health.
As authorities delved into the heartbreaking discovery, details emerged that shed light on the series of events leading up to the couple’s demise. Dr. Heather Jarrell, the Chief Medical Investigator, revealed that Hackman’s advanced Alzheimer’s disease and significant heart disease played pivotal roles in his passing. Amidst the harrowing circumstances, it was suggested that he may not have been aware of his wife’s demise in their home, underscoring the devastating toll of his declining health.
The distressing news sent shockwaves through the local community, prompting questions about hantavirus and its transmission. With hantavirus pulmonary syndrome (HPS) cited as the cause of Betsy Hackman’s death, concerns mounted about the potential risks posed by this rare but deadly disease. To shed light on this alarming development, here is a comprehensive guide to understanding hantavirus and its implications for public health.
Unveiling the Mysteries of Hantavirus
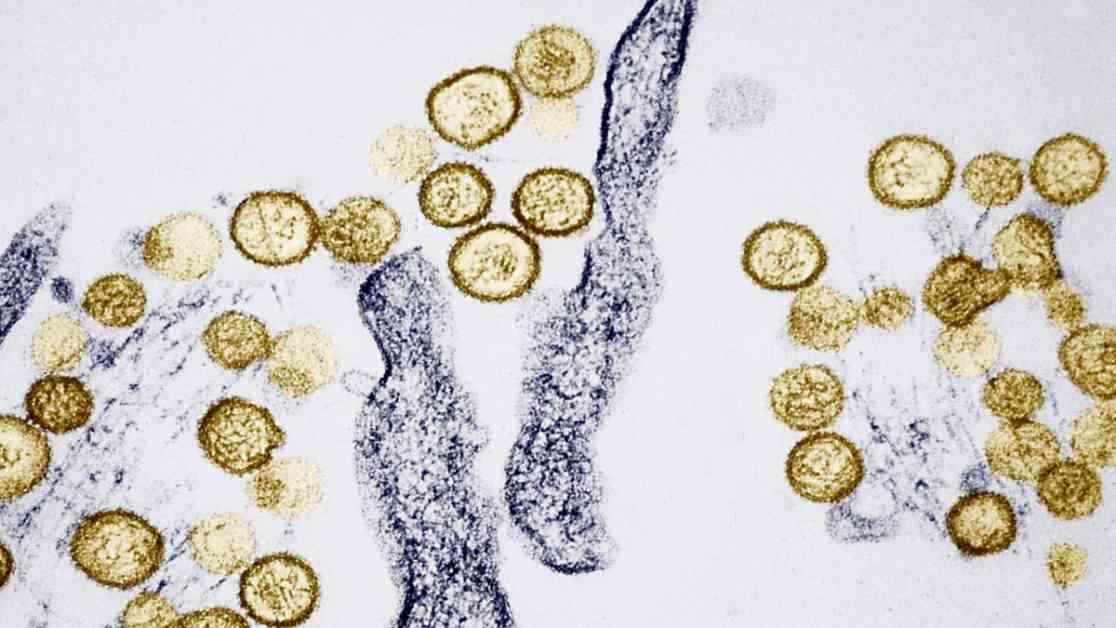
Hantavirus, a group of viruses transmitted through rodents’ body fluids and droppings, has garnered attention for its severe health implications. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) underscored the primary mode of transmission: inhalation of the virus, particularly through contaminated air. This method of exposure underscores the importance of vigilance in environments where rodents may be present, as the consequences of hantavirus infection can be dire.
The United States is home to various hantaviruses, with most leading to HPS, a condition that targets the cardiopulmonary system. The initial onset of HPS mirrors flu-like symptoms, which can rapidly progress to a severe illness characterized by respiratory distress. Timely intervention is crucial, as HPS carries a high fatality rate, with nearly 40% of infected individuals succumbing to the disease. The urgency of early treatment underscores the critical nature of prompt medical attention in mitigating the impact of hantavirus infection.
Navigating the Risks and Prevention Strategies
Understanding the risks associated with hantavirus exposure is paramount in safeguarding public health. Individuals who come into contact with hantavirus-carrying rodents or their biological materials are at risk of contracting HPS, regardless of their health status. The prevalence of rodent infestations in residential settings underscores the need for proactive measures to minimize the likelihood of exposure.
Deer mice, a common carrier of hantavirus in the U.S., serve as a primary source of transmission for HPS. Various pathways exist for contracting the virus, ranging from inhalation of contaminated air to direct contact with infected rodents. Vigilance in handling potentially contaminated objects and maintaining a clean living environment are essential steps in reducing the risk of hantavirus infection. While cases can occur in diverse settings, rural areas with significant rodent populations pose a heightened risk, necessitating proactive measures to safeguard against exposure.
As the community grapples with the tragic loss of Gene Hackman and his wife, the specter of hantavirus serves as a stark reminder of the importance of public health awareness and preventive strategies. By understanding the nature of hantavirus transmission and implementing proactive measures, individuals can minimize the risk of exposure and protect themselves from this insidious threat. In times of uncertainty, knowledge and vigilance serve as potent weapons in combating the spread of hantavirus and safeguarding the well-being of communities nationwide.